Understanding Cryptocurrency For Beginners

Important Things to Understand This guide is about how to buy cryptocurrency for beginners in 9 easy steps. You will learn how to get started in investing in digital assets like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other cryptocurrencies safely and securely step-by-step. An In-depth Understanding to Begin With Crypto-Currencies The thought behind digital money is to utilize cryptography close by a calculation to control the creation and exchange of significant worth, as opposed to depending on focal experts. This implies you can send.
The Simplest Way I can Describe Everything You Need to Know About Cryptocurrency
Here is a guide to cryptocurrency for beginners. We offer simple answers to questions like what is cryptocurrency, how does it work, what is Bitcoin, what is blockchain, how do I buy cryptocurrency, etc.
Metaphor: Cryptocurrency is a bit like online banking without a central bank. It is software-based, like an online banking platform. There is a ledger (called a blockchain), balances, and account numbers. You access your balances by using a password and can make transactions this way. Just like with online banking, you don’t need to know how it works under the hood to use it.
What is Cryptocurrency? Cryptocurrency is a type of digital asset that functions as a currency. The system that makes a cryptocurrency possible is based on cryptography (“crypto”) and a cryptocurrency is meant to be used like a currency (“currency”). With that in mind, not every digital crypto asset is meant to be used as a currency like the popular cryptocurrency Bitcoin is.
What is Bitcoin?Bitcoin is a software file stored on computers across the world that acts as a ledger of financial transactions called a “blockchain.” The ledger contains account numbers called “public addresses” associated with balances of Bitcoin. People can move around balances of Bitcoin if they have the passwords (or “private keys”) to those accounts using software called a “cryptocurrency wallet” (see description below). Bitcoin is the name of both this system and its unit of the currency. You can phrase it like this, “balances of Bitcoin tokens are moved around on the Bitcoin blockchain by creating transactions in Bitcoin wallets.”
What is Blockchain? Technically Blockchain is first and foremost a database protocol (a set of rules) for sorting data into “blocks,” but it’s easier to think of a Blockchain as a type of database. Essentially, it is a spreadsheet where data is stored in cells (or “blocks”) that are linked together in order by cryptographic codes called “hashes.” This database is generally decentralized and distributed on many computers instead of being stored in one central location or managed by one central entity. In Bitcoin, blockchain is generally used to describe both the public ledger where all transaction data is stored and technology (the protocol) behind the ledger. Many who aren’t believers in Bitcoin as a currency / digital asset are supporters of blockchain technology and its many applications both within finance and beyond.
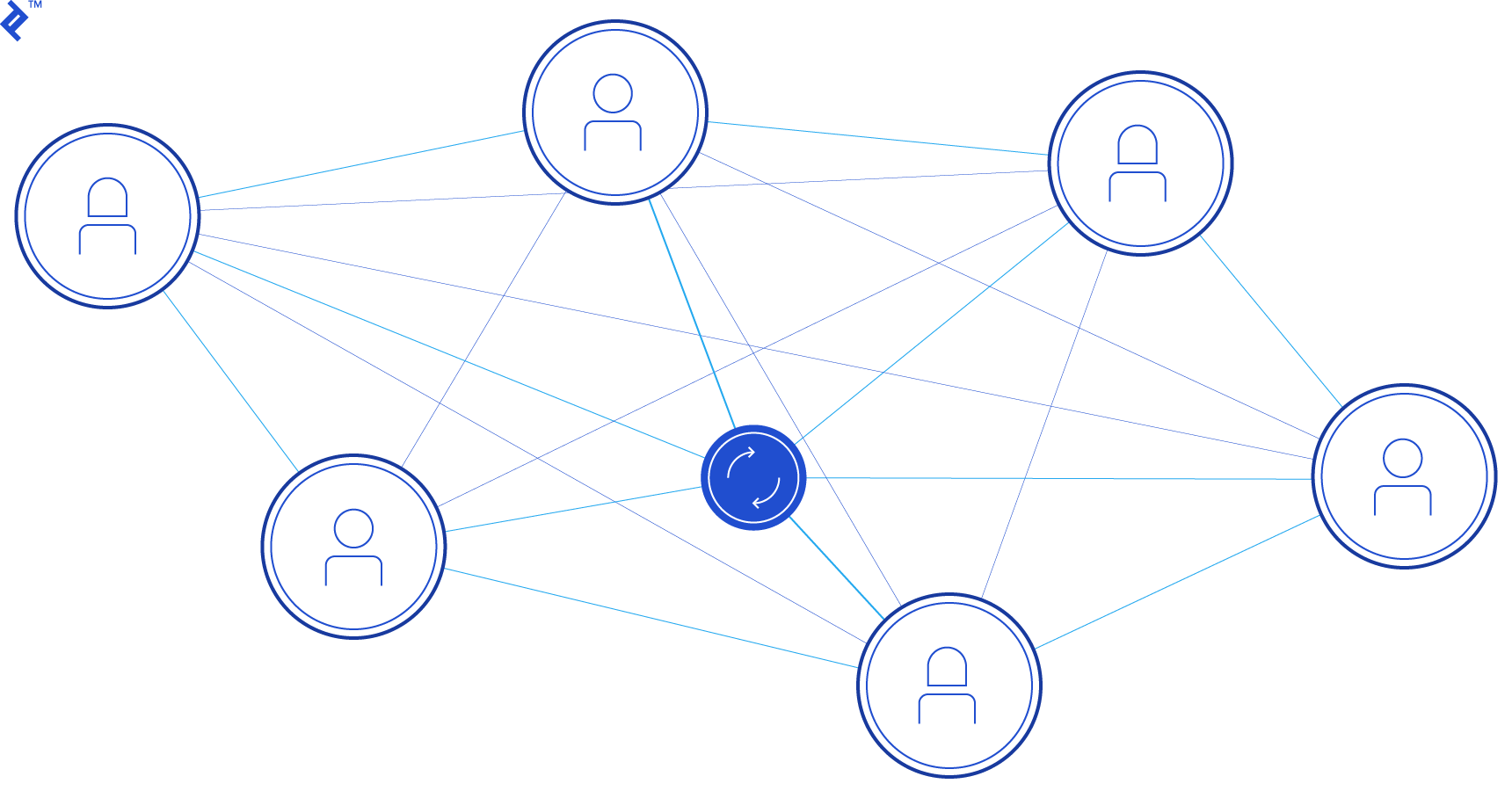
On Being Decentralized and Distributed. Instead of Bitcoin being hosted on one computer or one company’s computers, Bitcoin is hosted on many computers by many different entities (it is distributed). Meanwhile, everything is either done democratically or is controlled by algorithms, so there isn’t a need for a “centralized” middle-man like a bank or government (it is decentralized). Bitcoin’s blockchain is in this sense both decentralized and distributed.
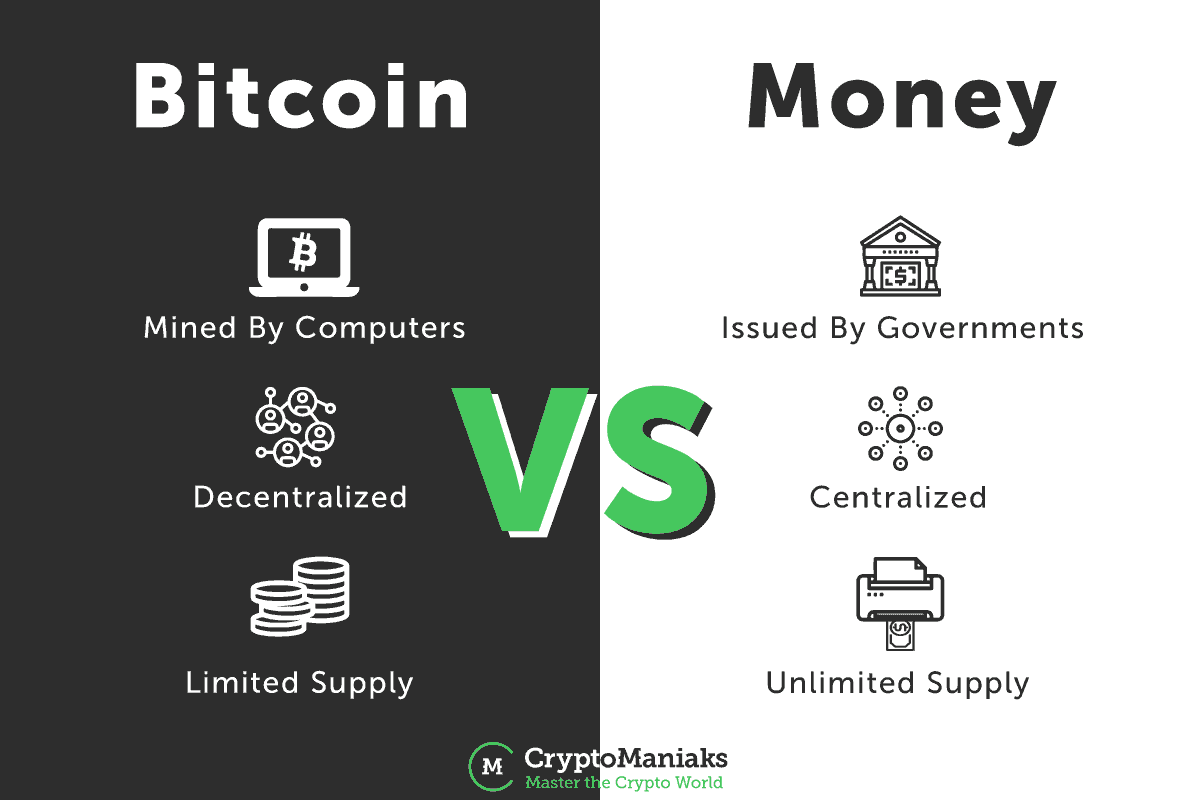
How is Cryptocurrency Different From Fiat Currency?Fiat currency, like the U.S. dollar, is controlled by central banks and controlled by states. It is legal tender and you can pay your taxes with it. Cryptocurrency, like Bitcoin, isn’t controlled by a central entity… but it isn’t legal tender and you can’t pay your taxes with it. Otherwise both fiat currencies and crypto currencies act as mediums of exchange and stores of value. With that in mind, some argue that cryptocurrency is a digital asset with exchange value, but not a true currency.
Can I buy things with Cryptocurrency? Cryptocurrency can be used as a payment method for any good or service that accepts cryptocurrency. The most common cryptocurrency used as payment is Bitcoin. As time goes on, accepting Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies as payment is becoming more common. Check out a list of things you can buy with Bitcoin.
What are the Benefits of Using Cryptocurrency as a payment method? There are a number of benefits of cryptocurrency as a payment method. The main benefits of cryptocurrency in this sense are the often low transaction costs and quick transaction fees compared to other payment systems. On a good day cryptocurrency is the quickest and cheapest way to send money around the globe (XRP is a great example of this). Cryptocurrency is also an easy way to make payments online, especially for peer-to-peer transactions. Another big benefit is that cryptocurrency doesn’t require trust, which removes potential worry for both the sending and receiving party. Meanwhile, for some people in some states, cryptocurrency can act as an alternative to a states’ currency (which can be good if that currency is suffering from rapid inflation for example).
How do I Buy / Sell Cryptocurrency? One can buy and sell cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin via online brokers or exchanges like Coinbase or GDAX. Exchanges are like digital stock exchanges, but for cryptocurrencies. Learn how to trade cryptocurrency or check out our cryptocurrency investing starter kit.
Is Cryptocurrency Legal? In general, cryptocurrency is legal in every respect in the U.S. and much of the world. The only rules of thumb are 1. you have to pay taxes on it and 2. anything that would be illegal otherwise is also illegal with cryptocurrency.
Is Cryptocurrency Taxable in the U.S.? Cryptocurrency is taxed as an investment property, that means you have to tally profits and losses at the current market value of a cryptocurrency when you sell it, use it, or trade it and then pay the capital gains tax on profits in a calendar year. Please take time to learn about the tax implications of cryptocurrency.
What is an ICO? An ICO is an initial coin offering, a way for a new coin to raise money by offering a pre-sale of an up-and-coming token. ICOs are controversial. On one hand, some ICOs have been scams, on the other hand some states have worried that ICOs are mimicking securities without following the securities rules. One should do extra research before participating in an ICO.
What is a token? Token is a word that has a few different meanings in cryptocurrency. In simple terms, it just describes a cryptocurrency and its unit of value (a cryptocurrency = a token). For example one could say “I have 10 Bitcoin tokens.” The term is also sometimes used to describe cryptocurrencies existing on other coin’s networks. For example, the KIN ICO is a token on the Ethereum network. Lastly, encrypted bits of data that don’t contain identifying information are also called “tokens,” this type of token is also used in cryptocurrencies. In other words, what the term means depends on context.
How Do Transactions Work? Software called a cryptocurrency wallet (see below) is used in conjunction with an account number and password (technically public address and private key). The private key (known only to its owner, like a password) is used to create a signature that allows the owner to move around funds on the blockchain. Transactions are then secured on the blockchain in sequential blocks by “miners” (see the next section). Almost all cryptocurrencies work like this.
How Do I Store Cryptocurrency? In overly simple terms, you essentially “store” cryptocurrency in cryptocurrency wallets (see the next point for the technical details). For long term, you’ll likely want a “cold wallet”(where you store your private keys offline). For short term use, you might use a range of options or even temporarily keep funds on an exchange (but be careful, if it is connected to the internet, it is a “hot target”).
What is a Cryptocurrency Wallet? A wallet can be thought of as software that allows one to store cryptocurrency and create cryptocurrency transactions. This is a simple way to think of a wallet even though cryptocurrency isn’t technically stored in a wallet (instead public addresses are associated with transactions recorded on the blockchain, and thus are associated with balances, which the wallet software can read and display for you). More technically then, a wallet is software that allows you to store your private keys, view balances associated with public addresses, and create and sign outgoing transactions. With that noted, one must differentiate between wallets where you control your private keys (like the Bitcoin Core wallet), and custodial wallets where third parties host the wallet for you and are in control of the private keys (like the wallets on Coinbase or GDAX).
What is a Node? Since cryptocurrency is distributed many computers around the world have to run the software. Any computer running a copy of the software is “a node.” A full node runs a full copy of the blockchain.
How are New coins Created? When a transaction is created in a wallet it is broadcast to everyone in the Bitcoin network. For that transaction to be added to the ledger, users running mining software must solve cryptographic puzzles that let them add a block of transactions to the blockchain. The reward for adding a block is newly minted cryptocurrency. Thus “mining” is cracking puzzles to play digital accountant, and new coins are minted as rewards for mining transaction blocks.
How is Bitcoin Secure? Bitcoin is secure for two main reasons. 1. It uses a lot of one-way encryption that makes everything that is encrypted next to impossible to hack (it requires a ton of work). 2. It is distributed and so there is no central software to hack.
How does the cryptography aspect of Bitcoin work? At the core of Bitcoin, in terms of cryptography, is cryptographic hash functions. Key concepts include public-key cryptography and proof-of-work functions. If you want a crash course in the cryptography behind those terms, clicks those links and try reading the Bitcoin white paper: Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System.
What Happens If I Lose My Keys or if Someone Steals My Cryptocurrency? If you lose your private key, you lose access to the balances associated with it. If someone gets access to your crypto and they steal it, there is generally no way to resolve this issue. However, if you use a third party platform, like an exchange, and the exchange and not your account is hacked, then you might have recourse. The major exchanges tend to be good about reimbursing users in the case of a hack.

Understanding Cryptocurrency For Beginners Beginner
How Can I better Secure My Cryptocurrency? Since losing your keys and theft are real issues, it makes sense to follow some best practices of basic internet security. Keep your keys backed up offline (learn more about secure cold wallets), don’t store all your crypto in one location, be careful about URLs (make sure the URL is the real one), use a browser dedicated to crypto, use two factor authentication on any account you can, choose strong unique passwords, and don’t use your public email to log into your accounts. Taking just a few of these steps will go a long way to protecting you, taking none of these steps is asking for trouble. As a rule of thumb two-factor authentication is a must, so make sure it is enabled on all platforms that allow it! TIP: Although there are exceptions to this rule, the main security risk with the major cryptos isn’t the software (the software takes a ton of work to hack) or the major exchanges (the major ones are ensured, keep most of their funds in cold storage, and have security teams), it is people not taking care to secure their accounts.
Is Bitcoin Anonymous? Bitcoin is pseudo-anonymous. Every transaction is recorded on the public ledger (the blockchain), but no identifying data is used. Everyone can see the transaction and the public wallet address associated with it, but no one knows who made the transaction (unless that person or entity makes that information public). Other cryptocurrencies have more or less focus on privacy than Bitcoin. Some cryptocurrencies, like Monero are truly anonymous (in theory). With Monero, not even transaction data is public.
What is a smart contract? A smart contract is exactly what it sounds like, a “smart” (software-based and programable) “contract” (a set of conditions that when met execute the terms of the contract). Smart contracts can be written to a cryptocurrency’s blockchain to create a trustless contract (a peer-to-peer contract that doesn’t require a middle-man or trust). Unlike paper contracts a software contract can execute any function that can be executed by the software once conditions are met. This means in theory smart contracts can replace real contracts, but also do anything software can do. Ethereum’s system relies heavily on smart contracts, anyone can create a smart contract on Ethereum if they have the native Ether token to pay the fee for using the system. TIP: Bitcoin transactions are smart financial contracts, but Ethereum allows for smart contracts for much more than just financial transactions. Ethereum’s contracts can distribute new tokens, double as insurance contracts, or anything you can think of.
On Being Peer-to-Peer and Trustless. An important feature of cryptocurrency is that it is trustless. The encryption, code, blockchain, etc all comes together to allow for a trustless peer-to-peer distributed and decentralized system. That sentence might sound jargon-y, but it contains some important points. At the core, the idea is that all the aspects of cryptocurrency come together to create a system that doesn’t rely on trusting your peers or trusting a middle-man. Contracts written to the blockchain are written in stone, there is no need for trust or middle-men to ensure the execution of a contract once its conditions are met!
Crypto Terms: “FOMO” is fear of missing out (an emotional response to seeing the price move a lot and wanting in). FUD is fear, uncertainty, and doubt that can affect prices of assets. “HODL” is a misspelling of hold from an old forum post (it today means “hold on for dear life during big price movements”). A “hard fork” is like a fork in the road, a copy and paste of software that allows each copy to branch off in a different direction (when this happens with Bitcoin the ledger is duplicated along with balances, meaning people get the newly forked coins for free). An “Airdrop” is a method of distributing newly minted coins to the wallet addresses of current coin holders. See a list of crypto jargon.
Did I miss something or do you need something clarified? Just ask me a question in the comments below and I’ll answer it.
Cryptocurrency (Like Bitcoin) Explained Simply
We explain “how cryptocurrency works.” The goal of this guide is to teach beginners about blockchain and digital currencies (like Bitcoin).
Below we simplify things to make a somewhat complex system easier to understand. Do a site search, Google search, or see the links below to learn more about specific concepts.
What a new user needs to know: Cryptocurrency is roughly the equivalent of using PayPal or a Debit Card, except the numbers on the screen represent cryptocurrency instead of dollars. All a new user needs to do is set up a Coinbase account or download the Cash App to get started. With Coinbase users can buy, sell, send, receive, and store Bitcoin, Bitcoin Cash, Ether, and Litecoin (Coinbase provides an all-in-one wallet, broker, and exchange service making them a one-stop-shop for new users). With Cash App users can buy, sell, send, receive, and store Bitcoin.
The basic concepts are: To use cryptocurrency, you don’t need to understand it (any more than you need to understand the monetary system to use a debit card). However, if you want to understand cryptocurrency you need to understand the concept of digital currency, the concept of blockchain (both as a public ledger of transactions and a technology), and the concept of cryptography. After-all, cryptocurrency is a digital currency, where transactions are recorded on a public digital ledger called a blockchain, and every process along the way is secured by cryptography. The goal of this page will be to help you understand these things and how they connect.
Understanding Cryptocurrency For Beginners
Cryptocurrency works a lot like bank credit on a debit card. In both cases, a complex system that issues currency and records transactions and balances works behind the scenes to allow people to send and receive currency electronically. Likewise, just like with banking, online platforms can be used to manage accounts and move balances. The main difference between cryptocurrency and bank credit is that instead of banks and governments issuing the currency and keeping ledgers, an algorithm does.

What is cryptocurrency? Cryptocurrency is best thought of as digital currency (it only exists on computers). It is transferred between peers (there is no middleman like a bank). Transactions are recorded on a digital public ledger (called a “blockchain”). Transaction data and the ledger are encrypted using cryptography (which is why it is called “crypto” “currency”). It is decentralized, meaning it is controlled by users and computer algorithms and not a central government. It is distributed, meaning the blockchain is hosted on many computers across the globe. Meanwhile, cryptocurrencies are traded on online cryptocurrency exchanges, like stock exchanges. Bitcoin (commonly traded under the symbol BTC) is one of many cryptocurrencies; other cryptocurrencies have names like “Ether (ETH),” “Ripple (XRP),” and “Litecoin (LTC).” Alternatives to Bitcoin are called “altcoins.”
How does cryptocurrency work? Transactions are sent between peers using software called “cryptocurrency wallets.” The person creating the transaction uses the wallet software to transfer balances from one account (AKA a public address) to another. To transfer funds, knowledge of a password (AKA a private key) associated with the account is needed. Transactions made between peers are encrypted and then broadcast to the cryptocurrency’s network and queued up to be added to the public ledger. Transactions are then recorded on the public ledger via a process called “mining” (explained below). All users of a given cryptocurrency have access to the ledger if they choose to access it, for example by downloading and running a copy of the software called a “full node” wallet (as opposed to holding their coins in a third party wallet like Coinbase). The transaction amounts are public, but who sent the transaction is encrypted (transactions are pseudo-anonymous). Each transaction leads back to a unique set of keys. Whoever owns a set of keys, owns the amount of cryptocurrency associated with those keys (just like whoever owns a bank account owns the money in it). Many transactions are added to a ledger at once. These “blocks” of transactions are added sequentially by miners. That is why the ledger and the technology behind it are called “block” “chain.” It is a “chain” of “blocks” of transactions. TIP: I’ve just described how Bitcoin works and how many other coins work too. However, some altcoins use unique mechanics. For example, some coins offer fully private transactions and some don’t use blockchain at all.
How does blockchain work? The blockchain is like a decentralized bank ledger, in both cases, the ledger is a record of transactions and balances. When a cryptocurrency transaction is made, that transaction is sent out to all users hosting a copy of the blockchain. Specific types of users called miners then try to solve a cryptographic puzzle (using software) which lets them add a “block” of transactions to the ledger. Whoever solves the puzzle first gets a few “newly mined” coins as a reward (they also get transaction fees paid by those who created the transactions). Sometimes miners pool computing power and share the new coins. The algorithm relies on consensus. If the majority of users trying to solve the puzzle all submit the same transaction data, then it confirms that the transactions are correct. Further, the security of the blockchain relies on cryptography. Each block is connected to the data in the last block via one-way cryptographic codes called hashes which are designed to make tampering with the blockchain very difficult. Offering new coins as rewards, the difficulty of cracking the cryptographic puzzles, and the amount of effort it would take to add incorrect data to the blockchain by faking consensus or tampering with the blockchain, helps to ensure against bad actors.
What is cryptocurrency mining? People who are running software and hardware aimed at confirming transactions to the digital ledger are cryptocurrency miners. Solving cryptographic puzzles (via software) to add transactions to the ledger (the blockchain) in the hope of getting coins as a reward is cryptocurrency mining.
How does cryptography work with cryptocurrency? The keys that move balances around the blockchain utilize a type of one-way cryptography called public-key cryptography. The “hashes” (the one-way cryptographic codes that tie together blocks on the blockchain) use a similar type of cryptography. Meanwhile, transaction data sent and stored on the blockchain is tokenized (tokenization is a type of one-way cryptography that points to data but doesn’t contain all the original data). The key to understanding these layers of encryption which ensure a system like Bitcoin’s (some coins work a little differently) is found in one-way cryptographic functions (cryptographic hash functions, cryptographic tokens, and public-key cryptography are all names for specific, but related, types of one-way cryptographic functions). The main idea is that cryptocurrency uses a type of cryptography that is easy to compute one way, but hard to compute the other way without a “key.” Very loosely you can think of it like this, it is easy to create a strong password if you are in your online bank account, but very hard for others to guess a strong password after it has been created.
How does one obtain or trade cryptocurrency? Cryptocurrency can be obtained most of the same ways other types of currencies can. You can exchanges goods and services for cryptocurrency, you can trade dollars for cryptocurrencies, or you can trade cryptocurrencies for other cryptocurrencies. Trading is generally done via brokers and exchanges. Brokers are third parties that buy/sell cryptocurrency, exchanges are like online stock exchanges for cryptocurrency. One can also trade cryptocurrencies directly between peers. Peer-to-peer exchanges can be mediated by a third party, or not. Please be aware that cryptocurrency prices tend to be volatile. One should ease into cryptocurrency investing and trading and be ready to lose everything they put in (especially if they invest in or trade alternative coins with lower market caps). See cryptocurrency investing tips.
TIP: Like anything else in life, there are tax implications to trading or using cryptocurrency. Make sure you understand the tax implications. In short, you’ll owe money on profits (capital gains) and may owe sales tax or other taxes when applicable. Learn more about cryptocurrency and taxes.
To summarize the above:
- Cryptocurrency can be thought of as a digital currency like PayPal or bank credit (what you use with your credit or debit card).
- Cryptocurrency transactions and balances are recorded on a public digital ledger called a blockchain.
- Cryptocurrencies can be accessed through software called wallets (transactions are broadcast to the network to be added to the blockchain via transactions created in wallets). This can be equated to online banking (where you have account numbers and passwords and move funds between accounts).
- Cryptocurrencies can be bought through a broker or traded on online cryptocurrency exchanges (like a stock exchange).
- There are many other cryptocurrencies beyond Bitcoin (some of which are better defined as digital assets).
- Unlike bank credit, which represents a centrally controlled and issued fiat currency (like the US dollar), cryptocurrency is decentralized and thus not centrally controlled.
- Instead of a central powering controlling cryptocurrency, an algorithm and users themselves control cryptocurrency. The algorithm dictates how transactions work and how new coins are created, users create peer-to-peer transactions using software called wallets. Transactions are recorded on a public digital ledger.
- Those who confirm transactions by breaking cryptographic codes are called miners. Mining is a process that creates new coins.
- Of course, you don’t need to know any of that. All you need to do is set up a Coinbase account and use that to buy and sell Bitcoin, Bitcoin Cash, Ether, or Litecoin and to send and receive cryptocurrency. Just remember to pay your taxes.
Understanding Cryptocurrency For Dummies
TIP: If you find yourself interested in cryptocurrency, check out an exchange like Coinbase Pro and learn how to trade one cryptocurrency for another. Coinbase Pro is a Coinbase product.